Introduction
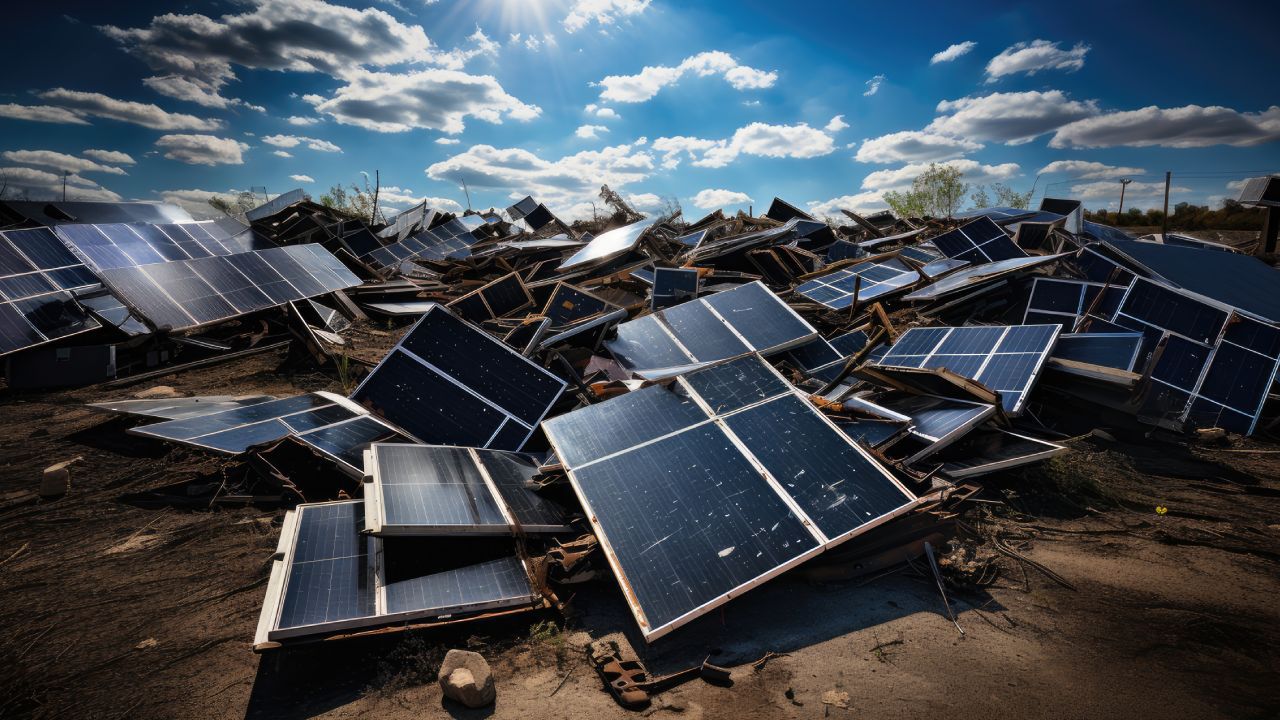
As Africa embraces renewable energy to tackle energy poverty and climate change, solar power has emerged as a frontrunner in the continent’s energy transition. With abundant sunlight year-round, solar energy provides a sustainable and affordable solution to Africa’s energy challenges. However, as the adoption of solar technology accelerates, a new concern arises: what happens to solar panels when they reach the end of their lifespan? This question underscores the urgent need for solar panel recycling in Africa, an issue that offers significant business and investment opportunities while addressing environmental sustainability.
Solar Energy Adoption in Africa
Africa’s energy landscape is rapidly evolving. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the continent’s installed solar capacity has grown exponentially over the past decade. Countries such as South Africa, Kenya, Nigeria, and Morocco are leading the charge, with significant investments in large-scale solar farms and decentralized solar solutions for off-grid communities.
Solar panels typically have a lifespan of 20 to 30 years. As early installations approach the end of their functional life, the volume of decommissioned panels is expected to rise significantly. Without proper recycling mechanisms, these panels could become a major environmental hazard due to their composite materials, including glass, metals, and potentially hazardous substances like cadmium and lead.
Why Solar Panel Recycling is Critical
- Environmental Protection: Solar panels are composed of materials that can harm the environment if not disposed of properly. Improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, undermining the very environmental benefits that solar energy aims to provide.
- Resource Recovery: Recycling solar panels allows the recovery of valuable materials such as silicon, aluminum, silver, and copper. These materials can be reused in manufacturing new panels or other products, reducing the need for virgin resources and lowering production costs.
- Economic Opportunities: The recycling industry has the potential to create jobs and drive economic growth. Establishing recycling facilities across Africa can stimulate local economies and create a sustainable supply chain for renewable energy components.
- Compliance and Sustainability Goals: As African nations implement stricter environmental regulations and international investors demand adherence to sustainable practices, businesses must incorporate recycling into their operations to remain compliant and competitive.
Current Challenges in Solar Panel Recycling
Despite its importance, solar panel recycling in Africa is still in its infancy. The challenges include:
- Lack of Awareness: Many businesses and consumers are unaware of the need for and benefits of recycling solar panels.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Africa lacks the specialized facilities and technologies required to process and recycle solar panels effectively.
- High Costs: The initial investment in recycling facilities and transportation logistics can be prohibitive, particularly in remote areas.
- Policy Gaps: Many African countries lack clear policies and regulations to govern the recycling of electronic and renewable energy waste, leaving the industry in a regulatory gray area.
Opportunities for Businesses and Investors
The solar panel recycling sector in Africa presents a fertile ground for innovation, entrepreneurship, and investment. Here are some avenues to explore:
- Setting Up Recycling Plants: Establishing state-of-the-art recycling facilities in strategic locations across Africa can position businesses as pioneers in this emerging industry.
- Developing Collection Networks: Building efficient collection and logistics networks is essential for aggregating decommissioned panels.
- Innovative Recycling Technologies: Investing in advanced technologies to enhance the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of recycling processes.
- Circular Economy Models: Integrating recycled materials into manufacturing processes, reducing waste, and lowering production costs.
Conclusion
The growing adoption of solar energy in Africa is a cause for celebration, but it also comes with a responsibility to manage the environmental impacts of decommissioned solar panels. Solar panel recycling presents a unique opportunity to align sustainability with economic growth. By investing in recycling infrastructure, fostering innovation, and enacting supportive policies, Africa can turn the solar waste challenge into a thriving industry.
For businesses and investors, the time to act is now. The solar panel recycling industry is poised to become a critical component of Africa’s renewable energy ecosystem, offering immense potential for profitability and positive environmental impact.